Business continuity for critical times
We provide implementation and management for Digital Solutions' continuity services programs, which include Business Continuity, Disaster Recovery and Crisis Management. These programs underpin delivery of the most critical activities of the University.
What is Business Continuity Management?
Business Continuity Management (BCM) is a holistic management process that identifies potential threats to an organisation and the impacts to business operations. BCM helps with the preparedness and mitigation of business continuity-related risk—this includes protecting the processes and resources that deliver the University’s core mission (teaching and research), which underpins the student experience (learning and outcomes).
BCM helps the University to continue delivering the products or services following a disruptive incident.
BCM lifecycle defines the stages of activity that an organisation moves through and repeats with the overall aim of improving resilience.
The three main components of BCM are:
- Business continuity
- Disaster recovery
- Crisis management
The BCM program addresses the recovery of Digital Solutions' delivered services so that critical operations and services are recovered in a timeframe that meets customer obligations, business necessities, industry practices, and regulatory requirements.
Digital Solutions’ BCM journey started in 2005 with the establishment of Disaster Recovery plans for business critical, high priority and medium priority systems and applications. Since then, DS has been incrementally building and updating DR plans for new emerging and existing systems respectively. Regular DR tests are performed to validate these plans.
In 2015, DS matured its BCM program to include Business Continuity and Crisis Management. This journey will be detailed in the sections below.
What is Business Continuity Management?
Business Continuity Management (BCM) is a holistic management process that identifies potential threats to an organisation and its business operations. BCM helps protect the processes and resources that deliver the University’s core mission (teaching and research), which underpins the student experience (learning and outcomes).
BCM lifecycle defines the stages of activity that an organisation moves through with the overall aim of improving organisational resilience. Our process mitigates risk so the University can continue to deliver products and services following a disruptive incident.
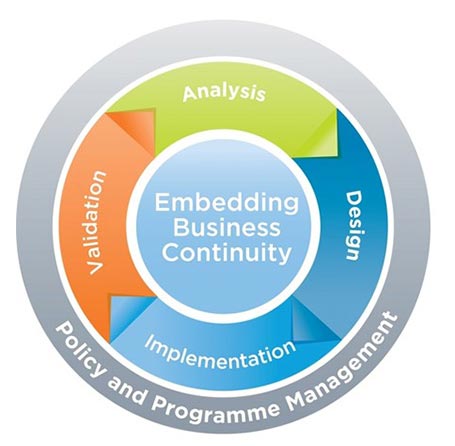
The three main components of BCM are:
- Business Continuity
- Disaster Recovery
- Crisis Management
Griffith's BCM program addresses the recovery of critical Digital Solutions' services in a time frame that meets customer obligations, business necessities, industry practices, and regulatory requirements.
Digital Solutions' BCM journey started in 2005 with the establishment of Disaster Recovery plans for business critical, high priority and medium priority systems and applications. Since then, we have been incrementally building and updating DR plans for new emerging and existing systems respectively. Regular DR tests are performed to validate these plans.
In 2015, Digital Solutions matured its BCM program to include Business Continuity and Crisis Management. Read details below.
Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery (DR) focuses on the IT or technology systems supporting critical business functions. DC Plans (DCP) involves a set of policies and procedures to enable the recovery or continuation of vital technology infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster. These plans include but are not limited to the recovery of relevant IT infrastructure, computer systems, network and communication elements, critical applications, human resources, physical assets, logistics, depended vendors, and cloud sourced critical system components.
Over the years, Digital Solutions has deployed multi-site disaster recovery strategies to cater for losing a single Data Centre; a single or multiple applications; loss of access to critical applications for a long period of time and failing over to an externally hosted Environment (Polaris) for Disruption Management. Besides staff familiarisation and awareness building, these recovery strategies has assisted in developing and maturing critical system data replication to a secondary Data Centre and improving and testing critical system Disaster Recovery plans regularly.
To support effective BCM, Digital Solutions has recently established an externally hosted environment to enable communication and access to limited critical services during the extreme event of simultaneous failure of both Gold Coast and Nathan data centres.
This external environment will provide authentication services to:
- access to Learning@Griffith (Blackboard)
- access to staff and student email (Gmail and Google drives)
- access to the Service Desk tool
- Single Sign On services that facilitate access to cloud hosted systems
CRISIS MANAGEMENT
Crisis Management (CM): encompasses processes to manage a wide range of crises like health and safety incidents, business disruptions, reputational damage. CM includes various plans like Crisis Management Plan (CMP), Crisis Communication Plan and Emergency Response Plans. Depending on the type of crisis, the response strategy may include invoking the Business Continuity (BC) or Disaster Recovery (DR) plans.
CMP is the governance structure to manage a major disruption and is critical in CM. It comprises of defining, designing, implementing and maintaining adaptable, scalable advance arrangements that can help respond to and manage a crisis. Digital Solutions has developed its ICT CMP that has been endorsed by the Office of Digital Solutions and University senior executives. DS’s CMP describes the roles and responsibilities of the Crisis Management Team (CMT) in addition to various crisis management processes.
DS’s CMT (listed below) has conducted multiple workshops emulating major crisis scenarios and responded and managed the situation by invoking the CMP.
View the list of the roles and responsibilities of CMT members and they can be contacted to report any crisis at any time.
DS's CMT will operate in conjunction with the University CMT and escalate relevant issues to the University CMT/Emergency Management Team to seek directions and provide situational reports (Sitreps).
Below is the six step process followed by the Digital Solutions CMT

6 Steps
- Crisis management trigger (what, when)
- Convene CMT (key people come together)
- Assess situation (seek and make sense of information)
- Identify what needs to be done (immediate, future) and agree on the Incident Action Plan (objectives, strategy)
- Coordinate and monitor response (delegate tasks)
- Review (defuse, debrief, improve)
A good, clear and targeted communication is very essential in a crisis situation. Digital Solutions' Crisis Communication Plan describes the best practices and effective communication templates that can potentially be used for fast and effective communication during a crisis. Proper communication will ensure that proper and consistent information reaches the stakeholders, and also help build an ongoing relationship with key stakeholders. Management of social media channels in a crisis is another significant factor due to its popularity and wide usage and must be carefully handled.
BUSINESS CONTINUITY
Business continuity (BC): involves identifying potential threats and impacts to the day to day operations of critical processes and creating a plan aiming to keep all essential aspects of the process functioning despite significant disruptive events.
In 2013 Griffith University established a Business Continuity unit and defined an initial list of critical processes (listed below)
- Enrolment
- Admissions (domestic and international)
- Timetabling (classes and exams)
- Teaching, learning and assessment
- Examinations
- Checking graduation eligibility
- Research and research grant applications
- Payroll
In order to align Digital Solutions' BCM program to the University’s critical processes, DS conducted a thorough detailed mapping of the above critical processes to identify potential DS processes to build Business Continuity plans.

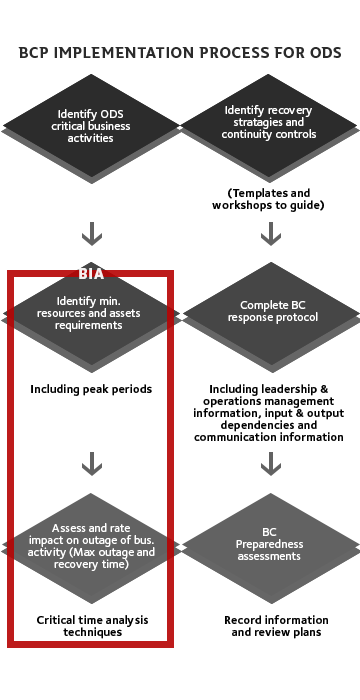
To date, Digital Solutions has identified 42 critical business processes. Business continuity plans are in place for 35 processes, and seven are under development. These plans are stored in the continuity repository and regularly updated.
Validation of these plans is a major component of any BCM program. Annual or regular testing of plans is a mandatory component of the ISO 22301 standard. In order to meet this requirement, Digital Solutions has scheduled its first table-top BCP Validation exercise in February 2018. Here, the BCP will be tested in detail by simulating a real life scenario.
Frequently asked questions
Is Digital Solutions' Continuity Services the only team responsible for BCM?
No. The Continuity Services team will coordinate and facilitate continuity exercises and BCP promotion. However, supporting and ensuring the University’s resilience is the responsibility of all the employees. BCM should be embedded to organisational practices such as Project Management, Change Management and Procurement.
What do I do if media or customer contacts me enquiring about the status of a disruption?
Never communicate to media or customers regarding the response or status of a disaster. A designated staff is responsible to communicate during these disruptive times. Point them to the responsible staff for communication.
How does the ODS BCM Program impact on the strategic goals of the University?
Effective BCM will ensure the continued operation of critical systems underpinning the learning and teaching programs, research activities and quality student experience.
Whom to contact during a disaster or if I am aware of an oncoming disruption?
First contact your line manager or team leader or send an email to ods-continuity@griffith.edu.au
Information for Project Management Office:
Any project that involves new or upgrading existing critical or high priority systems must have new or updated DR documents before project completion.
What are the benefits of BCM?
By supporting and practising BCM, Digital Solutions' strategy is aligned with:
- ISO 22301: Societal Security - BCM system requirements
- Griffith IT Plan 2013 - 2017 operational goal 10 - Resilience: mapped to University strategic priority # 4 – be a sustainable University
- Resilience strategy S10.6 – Develop and implement an IT BCM framework incorporating BC Planning and ITDR planning embedded in University BCM
- Compliance with the University BCP framework
- BCM is like an “insurance policy”, which will better prepare ODS in a disruption
Besides abiding to the above corporate strategies, by implementing a BCM Program, Digital Solutions can mitigate:
- operational impacts
- reputation impacts
- academic mission impacts
- loss of income
- loss of students
- regulatory impacts
- and more
It has been identified that an IT disruption of 19.7 minutes can cost an organisation $1,046,454.
118.8 minutes of disruption can cause a loss of $4,255,468. Proactive costs outweigh the reactive costs.
Familiarisation with recovery plans and processes is definitely beneficial during times of extreme stress and pressure.
Need help?
Need help:
Please forward queries or suggestions to ods-continuity@griffith.edu.auAccess the Service Catalogue to see the full list of available services.